Overview
The mirror that allows players to see their own avatar is a very important object in VRChat's social experience. Many users look for a mirror first when entering a world. However, mirrors are also one of the elements that have the greatest impact on world performance.
Therefore, implementing mirrors not just by placing them, but enabling them only when needed and allowing performance/quality balance adjustment, is essential for creating comfortable worlds.
This article explains how to control the VRCMirrorReflection component with UdonSharp to build a practical mirror system with on/off functionality and quality settings.
Step 1: Setting Up the VRCMirrorReflection Component
- Create Object: Create a
Quadin the scene to serve as the mirror's reflective surface.Quadfaces forward (Z+) by default, so it can be used as a vertical mirror without rotation. Note: If you use aPlaneand rotate X by -90 degrees, the mirror image may appear upside down. - Add
VRCMirrorReflection: Add theVRCMirrorReflectioncomponent to the created object. This alone makes the object function as a mirror. - Set Initial State: For performance, it's common to have the mirror GameObject inactive by default. That means unchecking the checkbox at the top left of the Inspector.
Key VRCMirrorReflection Settings
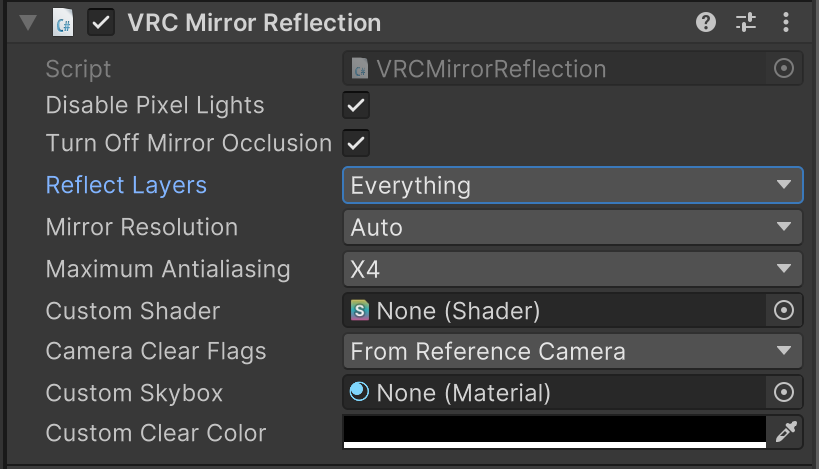
m_ReflectLayers: Selects which layers of objects to reflect in the mirror. By default, it reflects everything, but limiting it to just thePlayerlayer, for example, creates a mirror that only reflects player avatars (useful for dance practice), greatly reducing load. Note: TheWaterlayer is not rendered in mirrors.m_DisablePixelLights: Whentrue, pixel lights (Point Lights, etc.) are disabled in mirror rendering, reducing load.- Mirror Resolution: The mirror's resolution setting.
Automatches the user's HMD or monitor resolution, but is limited to a maximum of 2048×2048. For VR, this is per-eye resolution. Lower values reduce load but result in coarser image quality.Unlimitedhas no limit but is very high load, so use with caution.
Example 1: Simple ON/OFF Button
A mirror with the most basic local control where clicking a button toggles the mirror's GameObject active/inactive. The mirror state only changes in each player's own environment and doesn't affect other players.
Unity Setup
- Create a mirror object and set it to inactive by default.
- Place a button (e.g., Cube) in the scene to control the mirror, and add
ColliderandUdon Behaviour. Set theInteraction Textto something like "Mirror ON/OFF".
Script: LocalMirrorSwitch.cs
using UdonSharp;
using UnityEngine;
public class LocalMirrorSwitch : UdonSharpBehaviour
{
[Tooltip("Assign the mirror's GameObject to control.")]
public GameObject mirrorObject;
public override void Interact()
{
if (mirrorObject != null)
{
// Toggle the mirror GameObject's active state
mirrorObject.SetActive(!mirrorObject.activeSelf);
}
}
}
Final Unity Setup
- Assign
LocalMirrorSwitch.csto the button's Udon Behaviour. - Drag & drop the inactive mirror GameObject onto the script's
Mirror Objectfield.
Now, each player can turn the mirror on/off for themselves at their own timing. This is essential functionality that should be in every world.
Example 2: Mirror System with Quality Settings
A more advanced mirror system that not only toggles on/off but allows selection of quality levels like "High," "Medium," and "Low." The layers reflected in the mirror change dynamically based on quality.
This implementation uses two scripts: a manager script and a button script.
Script 1: MirrorSystemManager.cs (Manager)
The central script that manages mirror state and quality settings.
using UdonSharp;
using UnityEngine;
using VRC.SDK3.Components;
public class MirrorSystemManager : UdonSharpBehaviour
{
[Tooltip("VRCMirrorReflection component of the mirror to control")]
public VRCMirrorReflection mirror;
// Layer mask definitions
private int highQualityLayers = -1; // All
private int mediumQualityLayers = (1 << 9) | (1 << 10); // Player and PlayerLocal only
private int lowQualityLayers = (1 << 10); // PlayerLocal (self) only
public void ToggleMirror()
{
if (mirror != null)
{
mirror.gameObject.SetActive(!mirror.gameObject.activeSelf);
}
}
public void SetQualityHigh()
{
if (mirror != null)
{
mirror.m_ReflectLayers = highQualityLayers;
}
}
public void SetQualityMedium()
{
if (mirror != null)
{
mirror.m_ReflectLayers = mediumQualityLayers;
}
}
public void SetQualityLow()
{
if (mirror != null)
{
mirror.m_ReflectLayers = lowQualityLayers;
}
}
}
Script 2: MirrorButton.cs (For Each Button)
Attach to each button to call the manager's methods when clicked.
using UdonSharp;
using UnityEngine;
public class MirrorButton : UdonSharpBehaviour
{
[Tooltip("Reference to MirrorSystemManager")]
public MirrorSystemManager mirrorSystem;
[Tooltip("Button action: 0=ON/OFF, 1=High, 2=Medium, 3=Low")]
public int actionType;
public override void Interact()
{
if (mirrorSystem == null) return;
switch (actionType)
{
case 0:
mirrorSystem.ToggleMirror();
break;
case 1:
mirrorSystem.SetQualityHigh();
break;
case 2:
mirrorSystem.SetQualityMedium();
break;
case 3:
mirrorSystem.SetQualityLow();
break;
}
}
}
Unity Setup Steps
-
Manager Setup:
- Create an empty GameObject (e.g.,
MirrorSystemManager) and attachMirrorSystemManager.cs - Assign the mirror's
VRCMirrorReflectioncomponent to theMirrorfield
- Create an empty GameObject (e.g.,
-
Button Setup (for each of the 4 buttons):
- Create a button using a Cube, etc., and attach
ColliderandMirrorButton.cs - Assign the manager object above to the
Mirror Systemfield - Set
Action Type:- ON/OFF button →
0 - High Quality button →
1 - Medium Quality button →
2 - Low Quality button →
3
- ON/OFF button →
- Create a button using a Cube, etc., and attach
m_ReflectLayers is of type LayerMask, but since it can't be handled directly in Udon, we construct the layer mask as an int type using bit operations. 1 << layer number creates a mask containing only that specific layer, and | (bitwise OR) combines them.
Summary
- Mirrors are very high load, so it's strongly recommended to have them off by default and implement functionality for players to optionally turn them on/off.
- The simplest implementation is toggling the mirror GameObject's
SetActive()in the button'sInteract. Local processing is sufficient for this. - By changing the
m_ReflectLayersproperty ofVRCMirrorReflectionfrom Udon, you can dynamically control what objects the mirror reflects. This enables quality settings based on performance and use case. - Handling layer masks in Udon requires knowledge of
inttypes and bit operations.
Consideration for performance is essential for providing a comfortable VRChat experience. Mirrors, in particular, are one of the elements with the greatest impact. Implementing a user-friendly mirror system can be considered an important responsibility of world creators.